It’s been almost a year since Google last updated its search quality rating guidelines.
Unlike previous changes to the Research Quality Guidelines, which introduced important new concepts (like the new E for Experience last year), THE latest updates to the search quality guidelines seem much more focused on user intent and needs being met.
Google is:
- Refine what it means to deliver high-quality search results.
- Help quality assessors understand why certain results are more useful than others.
This level of nuance may help explain why we see some volatility during major updates (as well as during periods outside of announced updates). algorithm updates).
If search quality raters have provided Google with ample evidence that its results are not meeting user expectations, this can lead to substantial intent changes during core updates.
Looking at search results for the same query, before and after major Google updates, makes a lot more sense when you understand the granularity with which Google approaches understanding the intent behind a query and what it means. have high quality, useful content.
Here’s a high-level overview of what’s changed in the latest update to the Research Quality Assessment Guidelines.
More tips on review page quality for forums and Q&A pages
Google has added a new block of text to explain to reviewers how to assess the quality of forum and Q&A pages, particularly in situations where discussions are either brand new or drifting into “combative”, “misleading” content. » or “spam”.
A forum page defaults to “average” if it is simply a new page that hasn’t had time to collect responses. But old, unanswered messages should be considered low quality.
Google mentions “decorum” a few times in this section, indicating that combative discussions that demonstrate a lack of respect should be considered low quality.
- It’s a good reminder that the quality of comments on a given page can impact the overall quality of content on that page, assuming Google can crawl and index the comment content. Often comments sections are neglected or unmoderated, and if they become problematic, insulting, or disrespectful, it can have a negative impact on an otherwise good quality page.


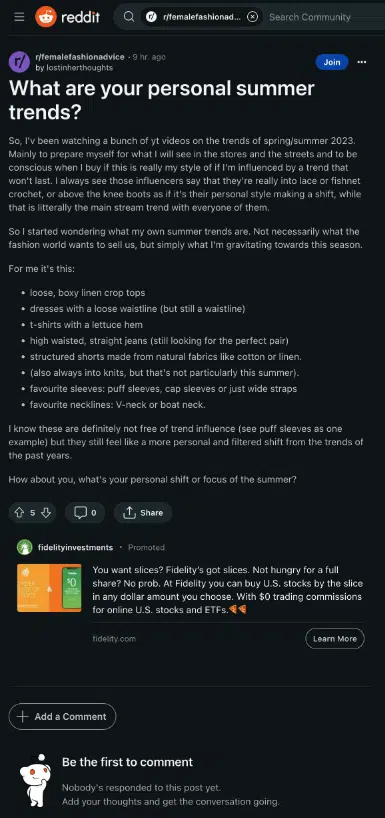
Additionally, the new version of the Search Quality Guidelines includes a visual example of what an “average” quality forum page on Reddit looks like. The question is only 9 hours old and has no answers, so it defaults to an “average” score.
It’s worth noting that Google is implying that there are no other low-quality features on this page that might otherwise tip the score toward “low quality” for new discussions.


Below is the example Reddit URL that Google used in this case:

A quick addition on the importance of a location in a query
Google added a short snippet about the importance of user location in understanding a query. For searches for nearby locations, location is important, while generic questions like “how does gravity work” have the same answer regardless of the user’s location.


- Interestingly, Google felt this nuance was worth adding to the reviewer guidelines. Although it seems obvious, it is true that the extent to which a search query has “local intent” built into it can have a major impact on the types of results that would best answer that query.
Develop “minor interpretations”
Google has added a more in-depth explanation of its definitions of “minor interpretations”.
Minor interpretations describe a situation in which a query can have multiple meanings and minor interpretations are the least likely to match the generally expected meanings of the query.
As part of minor interpretations, Google has introduced:
- “Reasonable minor interpretations” that help “fewer users” but are still useful for search results.
- “Improbable minor interpretations”, which are theoretically possible but highly improbable.
“No-chance interpretations” are interpretations of a query that are extremely unlikely for the user to search for. Google gives the example of “overheating pet” when the searcher types “hot dog” (although I think this interpretation is more plausible than a “no chance” rating!).


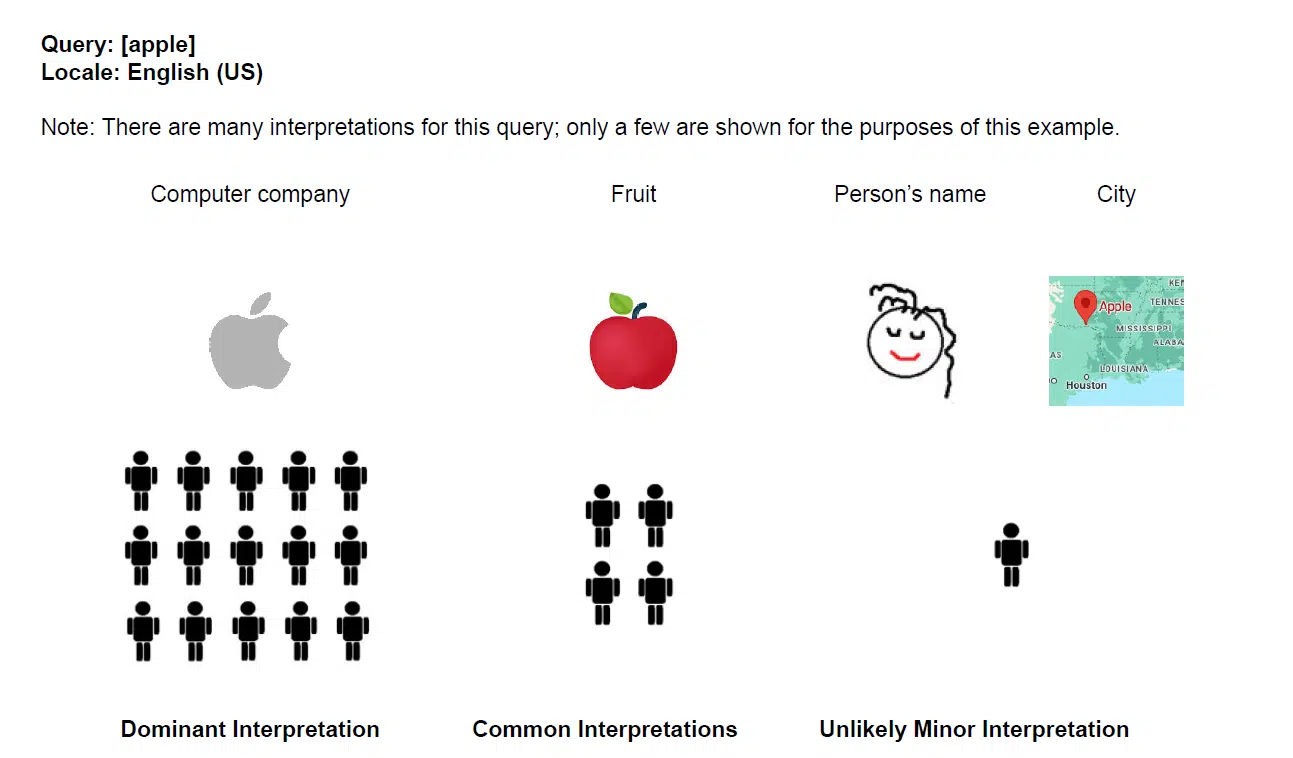
Google has also added new visual examples of how to interpret these definitions. For example, an “unlikely minor interpretation” of the search query “Apple” would be the US city, Apple, Oklahoma.

Further define the “Simple Know” and “Do” queries
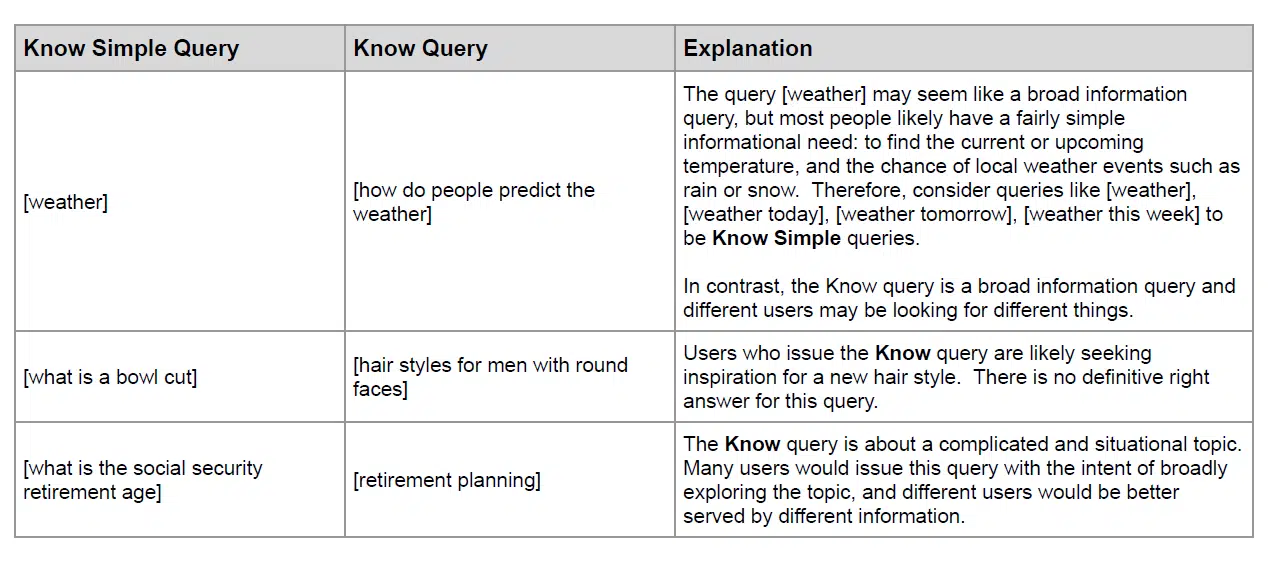
Google added several new sample query types not “Simple Know” queries.
“Simple Knowledge“Queries are defined as queries that look for a very specific answer, like a fact or a diagram, that can be answered in a small space, like one or two sentences.
Google added three new sample queries not Know Simple Queries: When users want to browse or explore a topic, find inspiration related to a topic, or seek personal opinions and views from real people.


What makes this addition interesting: The language used here is quite similar to that used by Google to describe the value of SGE (Generative Research Experience). For example, the following language is from the SGE main page:
- “Go deeper into a topic in a conversational way. »
- “Access the high-quality results and insights you expect from Google.”
- “I want to know what people think to help me make a decision”
Perhaps – and this is just speculation – the feedback Google receives from quality raters about whether queries can be classified as “Know Simple” (or not) can help them understand when to trigger SGE.
Along the same lines, Google added two new examples of “Know Simple Queries” and “Know Queries” – the last two rows of the table below – to provide additional context on when a query is easily answered or when the response is more open. .

Google has also added more example “Do” queries to the table below, starting with (shape of your video) and all queries below it. The three new examples represent queries that would be best answered with videos, images, or how-to guides.


Further refine user intent
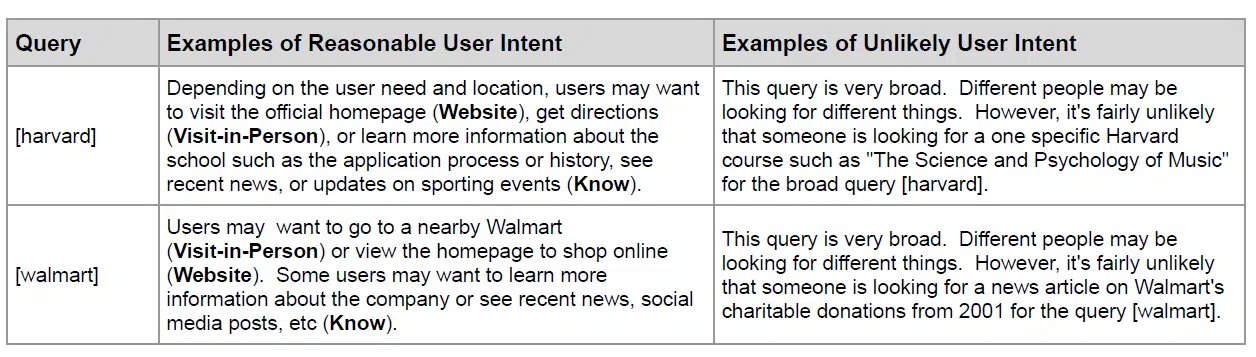
Google introduced new language around user intent by classifying what a unlikely user intent for a set of keywords.
In the table below, Google added a second column to explain the unlikely intents for the keywords Harvard and Walmart. This limits the intent of these keywords to a more reasonable user intent, rather than a completely open set of possible answers.
Users searching for “Harvard” may search for various details about the university, but are unlikely to be looking for a specific course.

Examples of Google SERP Features That Perfectly Meet User Needs
Google provides a table with various example search queries, user location, and user intent. It then displays the search result and evaluates the extent to which the result meets the user’s expectations (“Met Needs”).
Google also offers an explanation as to why these particular results are classified as “highly meeting” user expectations.
In this new version of the QRG, Google has added and adjusted some of the examples in the “Highly Meets (HM)” results, the highest rating possible to meet user needs “for most queries”.
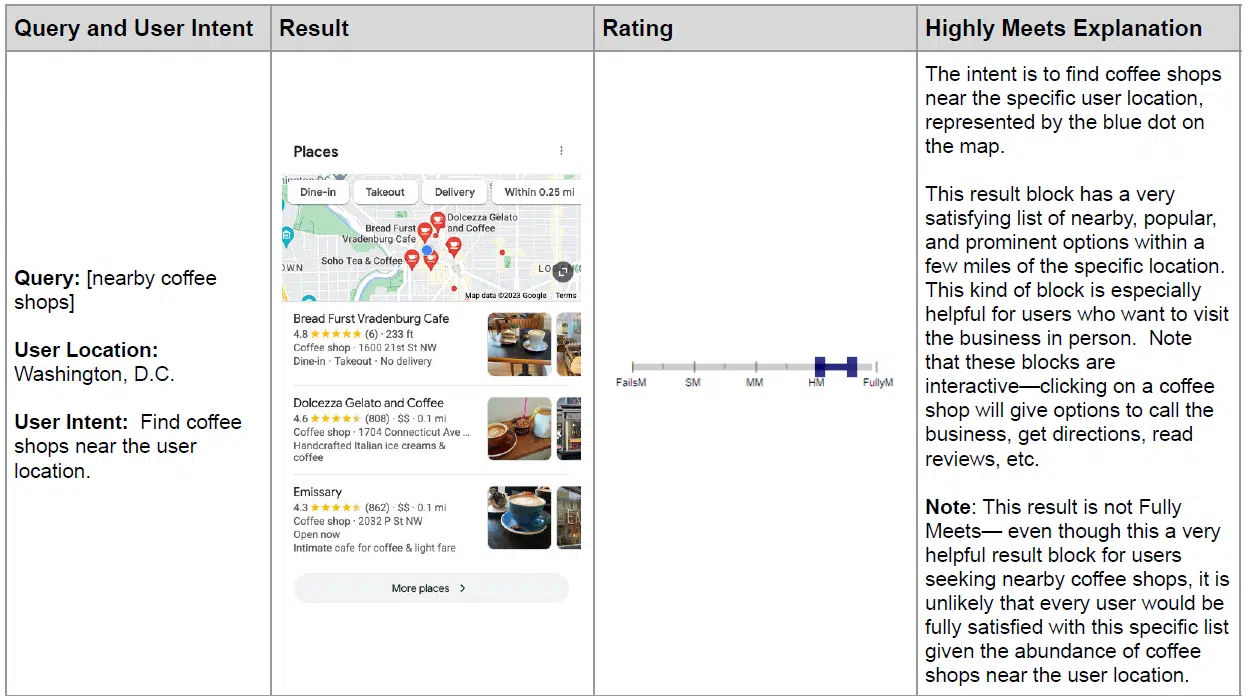
An example of a new example that Google has added to this list is when the user searches for “coffee shops near me”. Google provides a screenshot of a Google Maps local pack with three cafes listed and explains why this result strongly, but not entirely, meets the user’s expectations (it does not list all possible cafes).

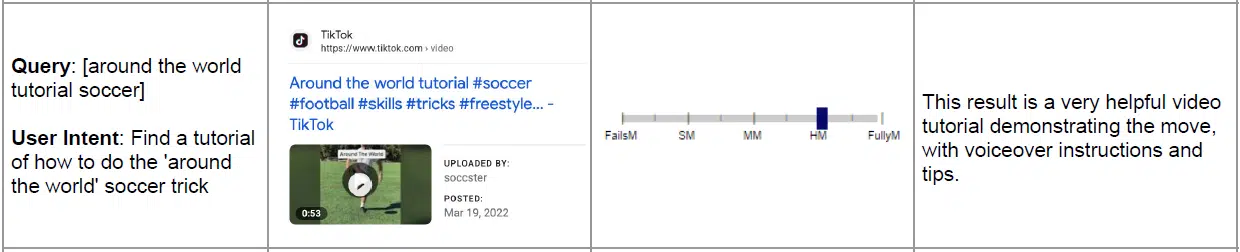
Google even added a TikTok video as an example result that perfectly meets the needs of users looking for a “around the world tutorial” for soccer.

These are just some of the new examples, which appear to provide a more modern view of different results, both from external sites and from Google’s SERP features.
Dig deeper. An SEO Guide to Understanding EEAT
The opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and are not necessarily those of Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
